Discoveries In Disease Diagnostics: Exploring The Ear Canal With GC X GC-MS
In today’s world, touched by a pandemic, we find ourselves lending more and more attention toward personal health and novel methods of diagnosis. One researcher,
Rabi Musah, and her team at the State University of New York State at Albany have discovered a new use for the cerumen found on your post-shower q-tip – medical diagnosis.
GCxGC-MS Analysis of Earwax
Earwax is a readily accessible biological matrix that has the potential to be used in disease diagnostics. However, its semisolid nature and high chemical complexity have hampered efforts to investigate its potential to reveal disease markers. This is because more conventional methods of analysis such as gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry yield unsatisfactory results due to the presence of many non-volatile and/or co-eluting compounds, which in some cases have very similar mass spectrometric profiles. In addition, these routine methods often require the sample to be saponified, which dramatically increases the complexity of the analysis and makes it difficult to determine which compounds are actually present versus those that are produced by saponification.
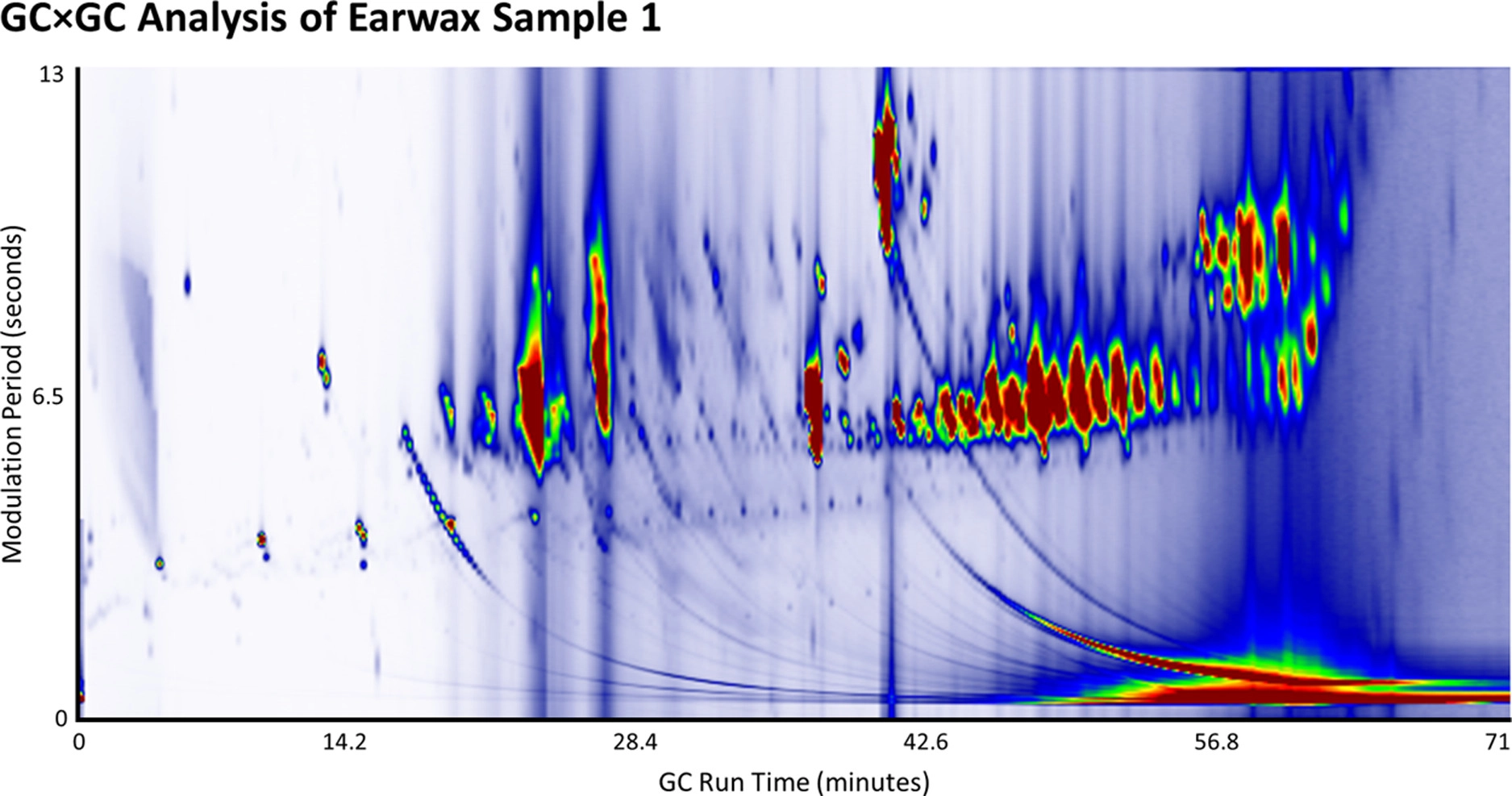
In
one study, led by Rabi Musah using JEOL’s AccuTOFTM GC-Alpha, two-dimensional GC mass spectrometry (GC × GC–MS) was successfully applied for the characterization of the chemical components of earwax from healthy donors using non-polar (primary) and mid-polar (secondary) columns without saponification. Over 35 of the compounds that were identified are reported for the first time to be detected in unsaponified earwax. The resulting GC × GC–MS contour plots revealed visually recognizable compound class clusters of previously reported groups including alkanes, alkenes, fatty acids, esters, triglycerides, and cholesterol esters, as well as cholesterol and squalene. The application of GC × GC–MS revealed results that provide a foundation upon which future studies aimed at comparing healthy donor earwax to that from individuals exhibiting various disease states can be accomplished.
Mass Spectrometry at JEOL USA
JEOL’s AccuTOFTM GC-Alpha, used for this research, is an orthogonal-acceleration high-resolution time of flight mass spectrometer which features an extended 4-meter flight path, mass accuracy of ≤ 1 ppb, and mass resolving power of ≥ 30,000. With a variety of available ion sources and direct probes, the AccuTOFTM GC-Alpha is a powerful and versatile high-resolution platform for GC-MS, GC x GC-MS and direct sample introduction.
JEOL boasts a suite of mass spectrometers ranging from the DART Ambient Ionization Toolbox™, which performs direct analysis in real time with limited sample prep, to the TQ4000, a GC-tandem quadrupole MS/MS system for rapid and high-sensitivity quantification of trace contaminants such as pesticides. Click here to learn more about our full mass spectrometry product offering.